Carbon accounting & Emissions calculation platforms help companies track, measure, and report their greenhouse gas emissions with accuracy. Developers design these digital offerings for sustainability managers, environmental consultants, and corporate executives, who must satisfy regulatory demands, reach net-zero targets, and make data-driven decisions about their environmental impact.
Today’s organizations face increased scrutiny to show environmental consciousness amid rising reporting requirements and stakeholder demands. A comprehensive system in turn replaces the manual, error-prone process and converts raw data of emissions into a useful form.
Together, these practices provide transparency into a company’s climate impact, enabling regulatory compliance and performance improvements. In this blog, we explain these concepts in depth, highlight key global standards (ISO 14064, ISO 14067, the GHG Protocol, PAS 2060), and show how enterprises can capture real business value by implementing robust carbon accounting and emissions calculation processes.
What Is Carbon Accounting?
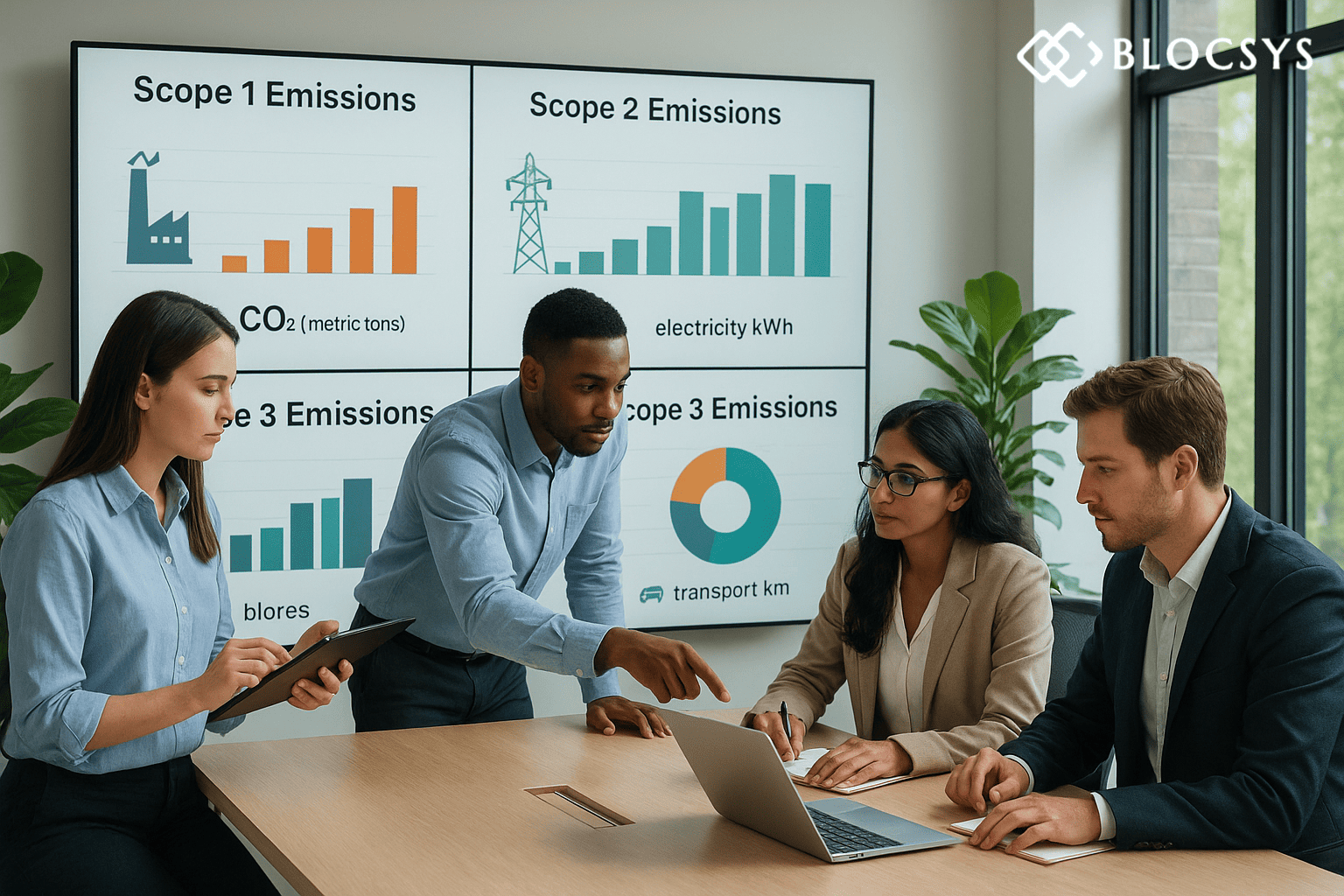
Carbon accounting is similar to financial accounting instead of tracking dollars, it measures climate impact. In practice, it involves tracking an organization’s total greenhouse gas emissions over time and across all operations. This includes emissions from on-site fuel use(Scope 1), electricity (Scope 2), and other indirect sources (Scope 3).
- By compiling this data into a GHG inventory, companies calculate their total greenhouse gas emissions and identify where those emissions come from.
- Regulatory Compliance: Emissions reporting is now required in many areas. ISO 14064-1 sets GHG reporting requirements, while the GHG Protocol helps businesses create a verified GHG inventory (ghgprotocol.org, iso.org). Strong carbon accounting guarantees that companies comply with these restrictions now and adjust to future climate policies.
- Market and Investor Expectations: Transparency is increasingly important to stakeholders. Studies show that investors may pay a premium for businesses with strong ESG records; meanwhile, over 75% of consumers favor sustainable brands Businesses increase brand equity and trust by monitoring and reporting pollutants.
Emissions Calculation: How It Works
Emissions calculation measures GHG output from activities, whereas carbon accounting is a continuous process. For instance, analysts multiply energy consumption by an emissions factor to calculate power-related emissions, covering all GHGs (CO₂, CH₄, N₂O, and fluorinated gases) within the organization’s boundaries.
To organize calculations, the GHG Protocol defines three “scopes”:
- Scope 1: The business generates emissions from direct sources it owns or manages for eg, fugitive emissions from refrigeration systems and combustion in boilers, furnaces, and automobiles.
- Scope 2: emissions come from the organization’s use of steam, electricity, heating, and cooling that it has purchased. The purchasing organization accounts for these indirect emissions based on consumption patterns, which occur at the location where electricity is generated.
- Scope 3: Emissions include all additional indirect emissions that take place along the value chain, such as:
- Activities upstream: capital goods, purchased goods and services, activities involving fuel and energy, transportation and distribution, operational waste, corporate travel, and employee commuting
- Activities downstream: Transportation and distribution, processing of sold products, use of sold products, end-of-life treatment, leased assets, and franchising
Many businesses expand to Scope 3 to address the complete supply-chain impact, but concentrating on Scopes 1 and 2 is a good place to start. Determining organizational boundaries, gathering activity data (mileage, energy consumption, etc.), applying the proper emissions factors (from the EPA, IPCC, or other databases), and adding up emissions from all sources are the main processes in the emissions computation process. Businesses frequently automate this procedure with software or specialized instruments. Precise emissions calculations are essential if data is not full, the footprint may be underestimated, which could result in “unintentional greenwashing”
Emissions Calculation: Step-by-Step Guide
These best practices may be used by firms to estimate emissions:
- Set the Organizational Boundaries:Determine whether to include all emission sources (Scopes 1–3) for completeness, and decide which facilities and operations to include, based on ownership and geography
- Gather Data: Gather activity data, i.e., fuel used, energy expended, volume produced, miles traveled, waste generated, etc. Reliable data sources are important; some use specialized computer programs or incorporate carbon accounting within enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems.
- Scale activity data by the standardized emission factors (e.g., kgCO₂ per unit of equivalent) for using emission factors. Local grid emissions data, national inventories, or global databases like the IPCC can be the sources of the factors.
- With these procedures, businesses have a systematic and traceable accounting of their carbon and emissions. By weaving the computational task into the fabric of everyday business (for example, on a monthly or quarterly basis) it becomes easier to monitor progress and identify where the work is inefficient and has too many moving parts.
Carbon Accounting Standards and Protocols
Carbon accounting and emission calculation are processes that are consistent with world standards.
Key frameworks include:
- ISO 14064 (Part 1 to 3): Details the requirements on how an organization quantifies and reports its greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. Inventories of organizations are covered in part 1 and verification in part 3. These criteria augment the relevance, transparency and accuracy (ISO).
- ISO 14067 (Product Carbon Footprint): Intended to quantify carbon footprints across the life cycle of the product and services. It helps companies support their product-level footprint claims (ISO). GHG Protocol
- (Corporate Standard): This is the most common international standard created by WRI and WBCSD. It covers all seven Kyoto gases and includes Scopes 1, 2 and 3 methodologies for reporting (GHG Protocol).
- PAS 2060 (Carbon Neutrality) – The British Standards Institution formulated PAS 2060 to specify the conditions under which an organization or individual can be declared carbon neutral and certified. Under this standard the organizations are required to estimate, reduce, and offset their greenhouse gas emissions.
By following these requirements, businesses create that their carbon accounting and emissions data are consistent and credible. Many regulations and voluntary programs use ISO 14064 or the GHG Protocol, putting compliance far into future reporting requirements.
Business Benefits of Carbon Accounting and Emissions Calculation
Benefits of Carbon Accounting A critical need to help business navigate complex regulation Though mandatory, rigorous carbon accounting is not just about a compliance checkbox.
- Regulatory & Carbon footprints open market opportunities through carbon credits and supply chain specs. Effective accounting helps organizations offset Scope 2 emissions and engage in green finance and ESG investments.This innovative approach helps to mitigate the risk of penalty which is attractive to investors seeking strong ESG practices
- Risk Mitigation: Accurate emissions data helps avoid greenwashing pitfalls. A 2021 survey by BCG found companies typically estimate with 30–40% error in their emissions calculations. Carbon accounting closes this “accuracy gap”, ensuring strategic decisions (like investments in efficiency) are based on real data.
- Efficiency & Cost Savings: Routine quantification of emissions uncovers waste.For instance, firms may learn that specific processes or equipment are too carbon-intensive. As a result, optimizing these hotspots can save money through energy efficiency while simultaneously reducing emissions.
- Brand and Reputation: Demonstrating genuine climate action strengthens brand equity.The report shows that business leaders use carbon accounting for compliance and to meet consumer and employee expectations . For example, 77% of consumers prefer sustainable brands, and two-thirds of employees value green employers .Public disclosure of assured emissions can build reputation and entice customers, partners, and staff.
- Carbon footprints create market opportunities through mechanisms like carbon credits and supply chain specs. With effective accounting, organizations can engage in sustainability markets, offset Scope 2 emissions, and prepare for green finance and ESG-linked investments.
Firms embracing carbon accounting report success: improved insights, cost-effective reduction targets, and annual benchmarking. For instance, a retailer reduced hidden emissions hotspots in its supply chain .These outcomes translate to both environmental and bottom-line successes.
Implementing Carbon Accounting with Blocsys Solutions
Construction of an integrated carbon accounting and emission calculation platform necessitates data consolidation, analytics, and reporting expertise. Blocsys Technologies can assist your company in developing an application that follows the above process and standards. Should your company require a dashboard to aggregate emissions data, automated calculation procedures, or blockchain traceability for green reporting, our professionals have the expertise.
- Personalized Development: Blocsys provides full-stack carbon management software development. From data model design (Scopes 1,2,3 included) to integration with IoT sensors or integration of ERP data feeds, we provide precise emissions tracking. Our solution integrates new emission factors and standard rules through calculation engines, thereby facilitating easy compliance with ISO 14064 and the GHG Protocol.
- Transparency & Security: Blockchain and smart contracts (our area of expertise) can be employed to form an unalterable record of emissions data. This builds trust between stakeholders and auditors. For example, every item of emissions data can be tagged in a secure ledger with a date/time stamp, allowing ease in auditing your carbon inventory.
- User Engagement: User experience-first solutions are our approach. Executive and engineer dashboards offer straightforward visibility into groups of emissions, targets to reduce them, and drill-down detail. Automated reporting and alerts enable teams to respond in real-time. We attempt to get carbon accounting out of data land and into action land.
Collaborating with Blocsys gives businesses expertise in technical solutions and sustainability. We ensure best-practice carbon reporting and support platform growth, including emission updates and GHG Protocol compliant. Our approach allows for quick deployment, enabling immediate emissions accounting.
Your Next Step: Build a Green Future with Blocsys
Effective carbon accounting and emissions calculation are now business imperatives. They drive efficiency, compliance, and credibility in a world where climate impact matters. To transform environmental data into strategic advantage, reach out to Blocsys Technologies. Our specialists are ready to contact you and craft a carbon management platform tailored to your needs.
Take the lead on sustainability: Contact Blocsys today to design your custom emissions calculation solution. Empower your business to manage its carbon footprint with confidence in ISO 14064, ISO 14067, GHG Protocol, and PAS 2060.
Blocsys has the expertise to help businesses create a complete carbon accounting, analytics, and emissions management platform.
Get started now: Reach the Blocsys team at https://blocsys.com/contact/ and put your company on the fast track to robust carbon accounting and emissions calculation.