Web3 represents the next evolution of the internet, built upon decentralized technologies like blockchain. It marks a fundamental shift away from the corporate-controlled web of today (Web2) toward a user-centric internet where individuals have direct ownership and control over their data and digital assets. This guide is for founders, technical leaders, and organizations in Web3, blockchain, and AI who need to understand this shift to build the next generation of digital infrastructure. We will cover the core technologies, practical use cases, and strategic decisions required to succeed.
From Reading and Writing to Owning
To understand what Web3 is, it helps to view the internet’s journey in three distinct stages, each expanding what users can do online. This is not just about faster speeds but a profound change in architecture, control, and value capture.
For founders and technical leaders, this evolution translates directly into new product capabilities that can unlock new markets and disrupt existing ones. The core idea is simple: we’re moving from a model where large corporations own the platforms and user data to one where users have verifiable ownership and a genuine stake in the services they use.
A Quick History of the Web’s Evolution
Looking back at the internet’s history puts the importance of Web3 into sharp focus. Each era was built to solve the problems of the one before it, leading us right to this moment.
- Web1 (The “Read-Only” Era, circa 1990s-early 2000s): This was the internet of static web pages. Information was mostly a one-way street, broadcast from a handful of creators to a massive audience of consumers. Think of it as a digital library—you could read anything you wanted, but you had almost no ability to interact or add to the collection.
- Web2 (The “Read-Write” Era, circa 2004-present): This is the social, interactive web we live in now. Companies like Facebook, Google, and Twitter built platforms that finally let users create and share their own content. It sparked a far more collaborative and dynamic internet. But this came with a trade-off: centralisation. These corporations control the platforms, own the user data, and capture nearly all the value created on their networks.
- Web3 (The “Read-Write-Own” Era): Web3 brings the final, missing piece to the puzzle: ownership. Built on blockchains, it allows digital assets—whether it’s currency, art, or data—to be verifiably owned and transferred without needing a central middleman. This injects a true economic layer directly into the fabric of the internet.
To make these differences crystal clear, let’s break them down in a table.
Web1 vs Web2 vs Web3: A Practical Comparison
This table breaks down the fundamental differences between the three internet eras from a technical and user-centric perspective, focusing on data ownership, architecture, and core functionality.
| Characteristic | Web1 (Read-Only) | Web2 (Read-Write) | Web3 (Read-Write-Own) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Interaction | Reading static content | Creating & sharing content | Owning & trading digital assets |
| Core Technology | HTML, HTTP, URLs | Social media platforms, mobile, cloud | Blockchain, smart contracts, tokens |
| Data Ownership | Controlled by website owners | Controlled by large tech companies | Owned by individual users |
| Architecture | Decentralised protocols | Centralised servers & platforms | Decentralised peer-to-peer networks |
| Value Capture | Captured by content publishers | Captured by platform owners (e.g., Google, Meta) | Shared among users, creators, & builders |
| User Identity | Anonymous (IP-based) | Platform-specific accounts (e.g., Google login) | Self-sovereign (crypto wallets) |
| Key Example | Personal blogs, GeoCities | Facebook, YouTube, Twitter | DeFi protocols, NFT marketplaces, DAOs |
As you can see, the shift to Web3 isn’t just incremental; it’s a complete re-architecting of the power dynamics online.
Web3 isn’t just a technological update; it’s an architectural and philosophical realignment. It returns control and ownership from centralised platforms to individual users, powered by decentralised networks that nobody owns but everyone can trust.
This move toward user ownership is far from a niche trend; it’s a powerful force shaping how modern digital systems are designed and built. To see how this is already playing out, you can learn more about how blockchain enterprise adoption is driving this business innovation and creating new opportunities for builders.
Ultimately, Web3 provides a fresh set of tools to create more equitable, transparent, and user-centric applications, from finance to digital identity.
Understanding the Core Pillars of Web3
To really get what Web3 is all about, you have to look past the hype and dig into the technologies that make it tick. These aren’t just abstract ideas; they are the actual building blocks for creating decentralised, user-owned applications. Think of them as the foundational layers of a new digital world, each with a critical job to do.
Together, these pillars—blockchains, smart contracts, and tokens—create an interlocking system that delivers transparency, automation, and true digital ownership. For any founder or engineering team looking to build in this space, understanding how they work together is the first step.
This map shows how we got here—from a static, read-only internet to the interactive social web, and now to the user-owned Web3.
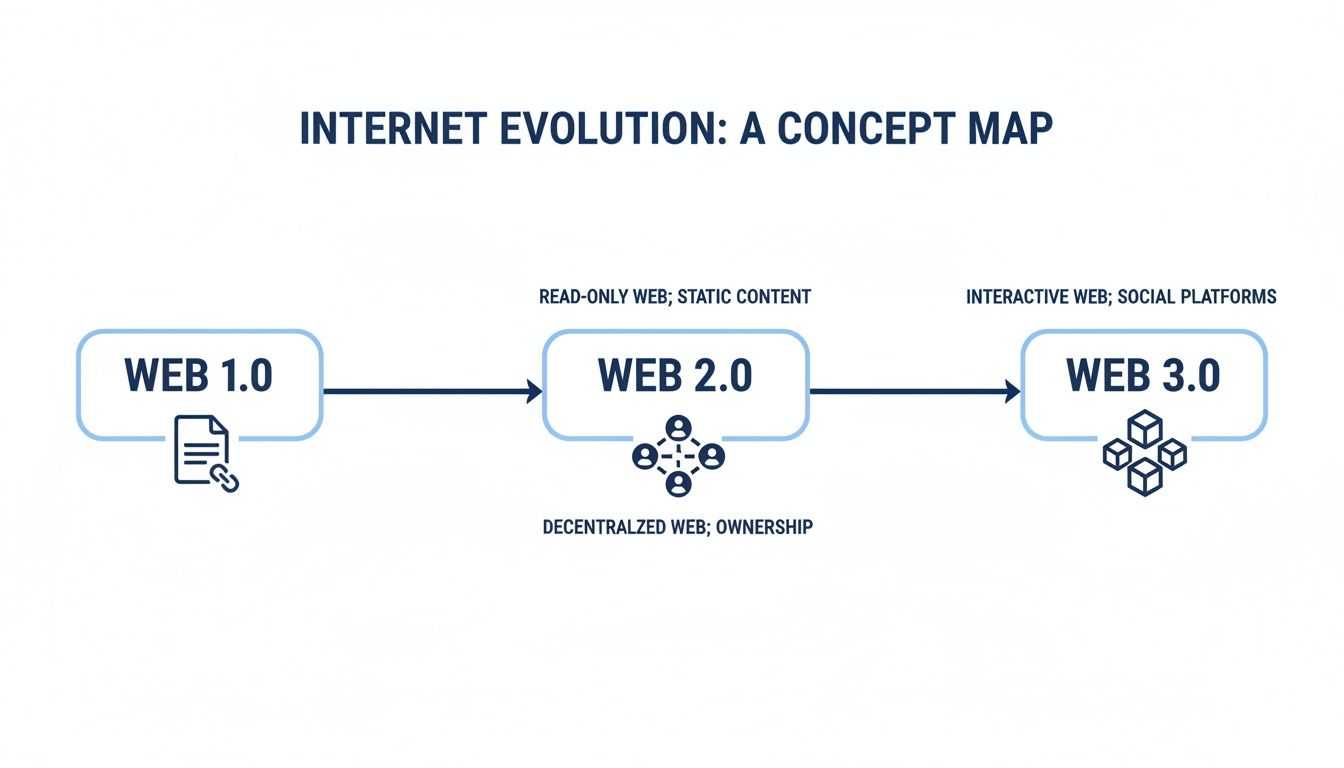
This evolution is all about shifting from just consuming information (Web1) and creating content (Web2) to actually owning verifiable assets (Web3). That shift is powered by the technologies we’re about to break down.
Blockchains: The Immutable Foundation
At the very heart of Web3, you’ll find the blockchain. A blockchain is basically a distributed, unchangeable public ledger where every transaction and piece of data gets recorded and verified. It’s a universal database that isn’t owned or controlled by a single company or government.
Instead of one central server, the database is copied and spread across a huge network of computers. This decentralisation is what makes it so secure. To change a record, a hacker would need to take over most of the network’s computers at the same time—a near-impossible feat. For builders, this means you can create applications where data integrity is guaranteed by the network itself, not by a corporate promise.
To fully appreciate the decentralised nature of Web3, it’s worth understanding the core principles of distributed systems that make it all possible.
Smart Contracts: The Automation Engine
If blockchains are the database, then smart contracts are the application logic. A smart contract is just a piece of code that runs on a blockchain, automatically executing the terms of an agreement when certain conditions are met.
Think of it like a digital vending machine. You put in a specific amount of crypto (the condition), and the machine automatically gives you the product (the outcome). There’s no cashier or middleman needed because the rules are coded directly into the machine.
A smart contract is essentially a self-executing API that runs exactly as programmed, forever, without needing a middleman. It automates trust, ensuring that all parties adhere to the agreed-upon rules without fail.
This automation opens the door to powerful use cases, from DeFi protocols that execute trades without a broker to decentralised insurance platforms that pay out claims automatically based on verified data.
Tokens: The Instruments of Value and Ownership
Finally, tokens are the digital assets that live on the blockchain. They represent ownership, value, or access rights within a specific application or network. Tokens are what make the whole “Read-Write-Own” idea tangible. They generally come in two main flavours:
- Fungible Tokens (like ERC-20 on Ethereum): These are interchangeable, just like currency. One Bitcoin is the same as any other, just like one dollar bill is identical to another. They’re mostly used for digital currencies, governance rights in a protocol, or utility inside an app.
- Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs, like ERC-721): These tokens are totally unique and can’t be replaced one-for-one. Each NFT represents ownership of a specific, one-of-a-kind asset—whether that’s digital art, a piece of virtual real estate, or a tokenised real-world asset like a property deed.
These three pillars—blockchains for secure settlement, smart contracts for automated logic, and tokens for representing value—work in perfect harmony. For example, an NFT marketplace uses a blockchain to record ownership, smart contracts to handle the buying and selling, and NFTs to represent the unique items up for grabs.
As you start building your Web3 product, understanding how these pieces fit together is non-negotiable. For a closer look, you might be interested in our guide on blockchain interoperability and powering cross-chain dApps.
The Essential Tech Stack for Web3 Applications
To turn the big ideas of Web3—decentralisation, smart contracts, tokens—into products people can actually use, you need a specific set of tools. This tech stack is the bridge between concept and reality, giving developers what they need to build platforms that are not just decentralised but also fast and user-friendly enough to win over mainstream audiences.
For any engineering team, picking the right components for this stack is a huge strategic decision. You’re constantly balancing speed, security, and cost. Let’s break down the essential layers that form the backbone of any serious Web3 project.
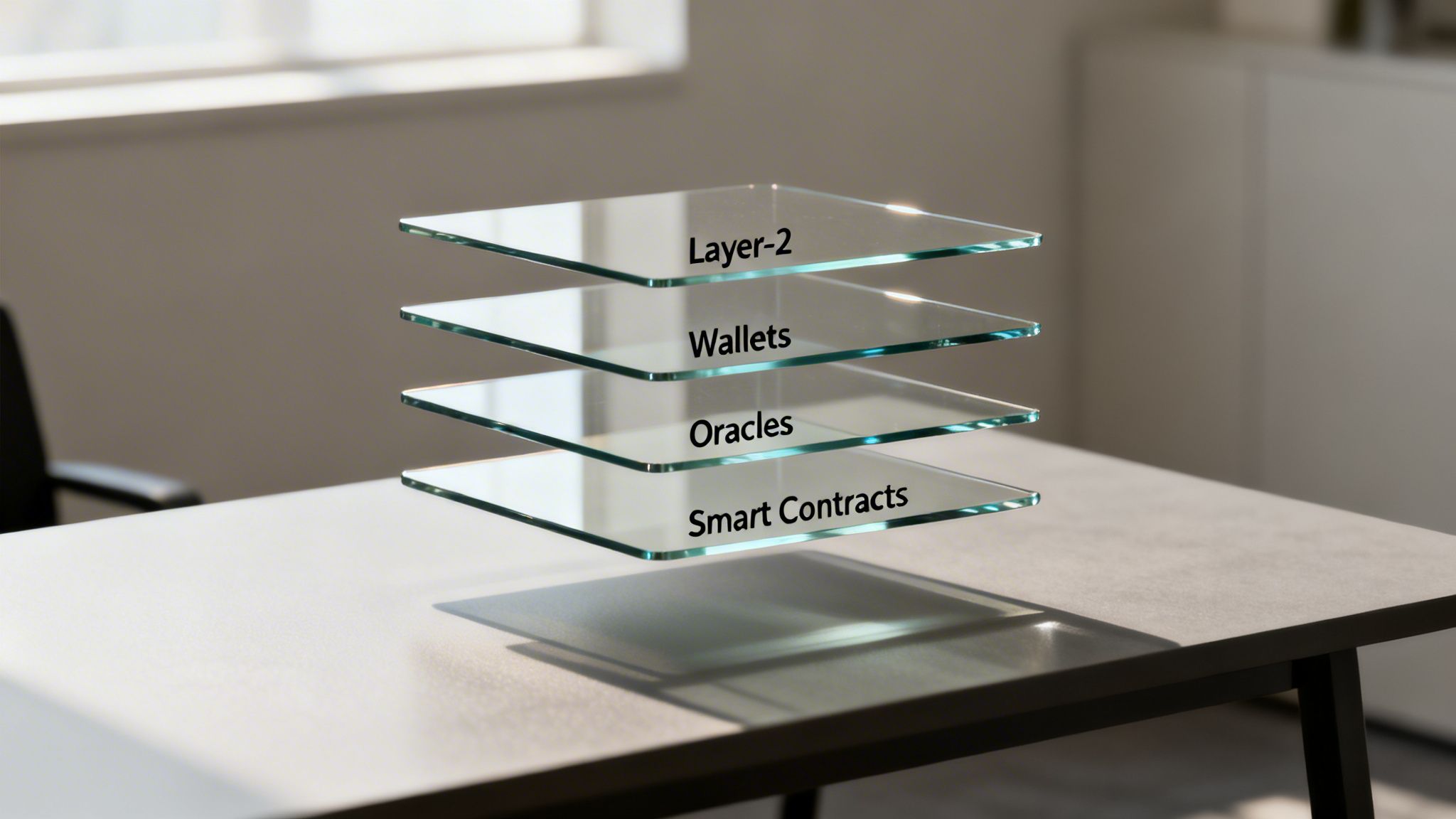
Layer-2 Scaling Solutions
One of the earliest and most painful roadblocks for blockchains like Ethereum was scale. The main network, or Layer-1, could only handle a handful of transactions per second. When demand spiked, the network clogged up, sending transaction fees (known as “gas costs”) through the roof and making users wait forever for confirmations. This made building anything high-volume, like a busy marketplace, completely impractical.
Layer-2 solutions were built to fix this. Think of them as express lanes built on top of the main blockchain highway. They handle most of the transaction processing off-chain, bundling everything up before settling it back on the main network. The result? Transaction speeds skyrocket and costs can drop by up to 99%.
Two main approaches dominate the Layer-2 space:
- Optimistic Rollups: These solutions bundle thousands of transactions together and “optimistically” assume they’re all valid. They post the batch to the main chain and open a challenge period where anyone can step in and flag fraud if they spot it.
- Zero-Knowledge (ZK) Rollups: This is a more complex approach that uses some clever cryptography to generate a “validity proof”—a mathematical guarantee that every single transaction in a batch is legitimate. This proof is posted to the main chain, inheriting its full security without needing a dispute window.
These technologies are non-negotiable for applications like decentralised trading platforms or NFT marketplaces that need to process thousands of transactions a day. For a deeper dive, you can explore the impact of Layer-2 solutions on blockchain scalability to see just how critical they are.
Wallets as Digital Passports
In the world of Web3, users need a way to manage their identity and assets without trusting a central company to do it for them. This is where wallets come in. A Web3 wallet is more than just a place to hold crypto; it’s a tool for storing digital assets, signing transactions, and interacting with decentralised applications (dApps).
It’s best to think of a wallet as a digital passport. It holds the user’s private keys—the secret cryptographic codes that prove ownership and give them the authority to do things on the blockchain.
Since wallets are the main gateway for users, their design and security are absolutely critical. They generally come in two flavours:
- Software Wallets (Hot Wallets): These are apps or browser extensions like MetaMask. They’re always connected to the internet, which makes them convenient for daily use but also more vulnerable to online attacks.
- Hardware Wallets (Cold Wallets): These are physical devices, like a specialised USB stick, that keep private keys completely offline. They offer the highest level of security because they’re insulated from internet threats, making them the standard for storing significant value.
Oracles Connecting Blockchains to the Real World
By their very nature, smart contracts are sealed off from the outside world. They can only access information that already exists on their own blockchain. This creates a huge problem: how can a smart contract react to real-world events, like a change in a stock price, the latest weather data, or the final score of a football match?
The answer is oracles. An oracle is a third-party service that acts as a secure bridge, fetching external, off-chain data and feeding it onto the blockchain so smart contracts can use it.
Oracles are the essential data couriers for Web3. They make smart contracts “smarter” by enabling them to react to real-world information, unlocking advanced applications like parametric insurance, RWA tokenisation, and dynamic prediction markets.
For example, a decentralised flight insurance platform might use an oracle to pull delay data directly from an airline’s API. If the oracle confirms the flight was delayed, the smart contract automatically gets the signal and triggers an instant payout to the policyholder. Without oracles, Web3 would be stuck in a closed loop, unable to interact with the vast amount of data that actually powers our world.
Real-World Web3 Use Cases That Solve Problems
Any new technology is only as good as the real-world problems it solves. Theory is one thing, but practical application is the real test. Fortunately, Web3 is already making that leap, creating a new generation of financial and market infrastructure that’s more transparent and efficient than anything that came before it.
These aren’t just futuristic ideas; they’re tangible business models being built and deployed right now. Let’s dig into some of the most impactful Web3 use cases and the specific pain points they address.

Real-World Asset and Carbon Tokenisation
For centuries, some of the world’s most valuable assets—real estate, fine art, private equity—have been stuck in a state of illiquidity. Selling them is slow, expensive, and often limited to a tiny circle of accredited investors. This locks up trillions of dollars in value that could be doing something productive.
Tokenisation shatters this old model. It works by creating a digital, fractional representation of a physical asset on the blockchain. This “token” can then be broken down into thousands of smaller pieces and traded on open markets, 24/7, by anyone.
- Problem Solved: Illiquidity and sky-high barriers to entry in traditional asset markets.
- Web3 Solution: A smart contract can lock the legal title of an asset (like a commercial building) and issue a fixed number of tokens representing fractional ownership. These tokens can then be bought and sold on decentralised exchanges.
- Outcome: Liquidity is unlocked instantly. Global participation becomes possible, and the huge costs tied to old-school asset transfers are slashed.
The same principle is now being applied to environmental assets. Carbon tokenisation puts verified carbon credits on-chain, creating a transparent, auditable, and global market for carbon trading. This makes it far easier for companies to fund climate projects and prove they’re meeting their sustainability goals.
The appetite for these on-chain solutions is growing fast. India’s Web3 ecosystem, for instance, has matured well beyond basic crypto trading and secured the top spot for on-chain adoption among over 150 nations. This growth is fuelled by practical use cases like DeFi, RWA tokenisation, and transparent supply chains, as detailed in a recent analysis of India’s real-world blockchain use on economictimes.com.
Decentralised Finance (DeFi) Platforms
The traditional financial system is powerful, but it’s also a maze of inefficiencies. It relies on a chain of intermediaries—banks, brokers, clearing houses—and each one adds cost, delay, and opacity to every single transaction.
Decentralised Finance (DeFi) rebuilds core financial services from the ground up using smart contracts on a blockchain. It completely cuts out the middlemen.
DeFi isn’t about replacing money; it’s about replacing the slow, centralised infrastructure that moves money. It uses code to automate functions that have historically required large, trusted institutions.
Here are a few powerful examples in action:
- Decentralised Exchanges (DEXs): Platforms like Uniswap use smart contracts to create automated liquidity pools. This allows users to trade digital assets directly from their own wallets without ever handing over custody to a central operator.
- Perpetual Trading Desks: These platforms let traders speculate on asset prices with leverage, all governed by transparent smart contract logic that automatically manages collateral and liquidations.
- Crypto OTC Systems: For large “block” trades, decentralised Over-The-Counter (OTC) systems use smart contracts as a trusted escrow. This guarantees both sides of a trade are settled securely and at the exact same time.
These systems crush counterparty risk, slash operational costs, and make financial services accessible to anyone with an internet connection—no matter where they are in the world.
Decentralised Prediction Markets
How do we accurately forecast the future? Traditional methods usually involve polls or a handful of experts, both of which can be biased and limited in scope.
Prediction markets take a radically different approach. They are open markets where anyone can buy and sell “shares” in the outcome of a future event. The market price of a share becomes a real-time indicator of what the collective believes will happen.
- Problem Solved: Inefficient and often biased methods for aggregating information and making forecasts.
- Web3 Solution: A smart contract creates a market for a specific question, like “Will a certain political candidate win the next election?”. Users can buy “Yes” or “No” tokens, and the price moves based on supply and demand.
- Outcome: You get a powerful, real-time mechanism for gathering intelligence. Because people have real money on the line, they’re incentivised to be right. The result is a market that taps into the “wisdom of the crowd” to produce surprisingly accurate forecasts.
From finance and asset management to information markets, these Web3 use cases are far more than just technological novelties. They are robust solutions targeting fundamental flaws in our legacy systems, opening up massive opportunities for founders and builders to create the next generation of market infrastructure.
Navigating Security and Regulation in Web3
Building a lasting Web3 product isn’t just about shipping innovative features; it’s about adopting a rigorous, security-first mindset from the get-go. While decentralisation opens up incredible possibilities, it also creates unique attack vectors and forces you to navigate a complex, ever-shifting regulatory world. For founders and engineering teams, treating security and compliance as an afterthought is a fatal mistake.
To launch a Web3 platform successfully, you have to manage risk proactively. This means locking down the application layer—especially your smart contracts—and making deliberate architectural choices around asset custody and future compliance. Get this wrong, and you risk catastrophic financial losses and reputational damage that you can never recover from.
Fortifying Smart Contract Security
Smart contracts are immutable. Once a contract is live on the mainnet, you can’t just patch its code. This is a double-edged sword: it guarantees execution, but it also means a single vulnerability can be exploited over and over until the funds are completely drained. A proactive, multi-layered security strategy isn’t just best practice; it’s your only real defence.
Your game plan needs to include a few non-negotiables:
- Professional Security Audits: Before you even think about deploying to mainnet, you absolutely must hire one or more reputable third-party firms to audit your smart contract code. This is mandatory. An expert, unbiased review is your best bet for catching critical vulnerabilities.
- Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Testing (VAPT): Audits are great for the code itself, but VAPT stress-tests your entire system. It simulates real-world attacks against your whole architecture, including off-chain components, to find weak points in your infrastructure.
- DevSecOps Integration: Security can’t be a final check-box. It needs to be woven into the fabric of your development lifecycle. This means running automated security checks, using static analysis tools, and enforcing secure coding standards from the very first line of code.
In Web3, security isn’t a feature; it’s the foundation. A single smart contract bug can erase millions in value instantly. A defence-in-depth approach—combining audits, testing, and secure development practices—is the minimum standard for protecting user assets and building trust.
Architecting Custody and Wallet Solutions
How users and your protocol manage private keys is one of the most critical architectural decisions you’ll make. It’s a decision loaded with trade-offs that directly impact user experience, operational security, and your project’s degree of centralisation.
Founders need to think hard about the main options:
- Self-Custody: Here, users have total control of their private keys using wallets like MetaMask. This lines up perfectly with the decentralised ethos, but it also offloads the entire security burden onto your users—many of whom aren’t equipped to handle it.
- Multi-Party Computation (MPC): MPC technology is a clever solution that breaks a single private key into multiple pieces, or “shards,” and distributes them. To sign a transaction, a minimum number of these shards must come together, which completely eliminates a single point of failure.
- Institutional Custody: If your platform is going to handle a serious volume of assets, partnering with a qualified, insured custodian is often the right move. They provide institutional-grade security, robust operational controls, and ready-made compliance frameworks.
Designing for Compliance Awareness
The global rulebook for digital assets is still being written, but the trend is undeniable: more oversight is coming. Building your system with future compliance in mind is a massive strategic advantage. It means designing modular systems where you can plug in Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) checks later on, without having to re-engineer your entire platform.
Beyond crypto-specific rules, Web3 projects still need to apply diligent Cyber Risk Management Best Practices to protect against common vulnerabilities. By building with a compliance-aware mindset from day one, you ensure your product is agile enough to adapt and thrive as the regulatory landscape matures.
How Blocsys Helps Organizations Build in Web3
Launching a successful Web3 product demands disciplined engineering and a clear, executable strategy to turn vision into reality. This is where architectural design, secure smart contract development, and scalable backend infrastructure become critical. Choosing the right engineering partner can be the single most important decision you make.
At Blocsys, we are a specialized engineering firm that helps startups and enterprises build the next generation of on-chain products. Our focus is on end-to-end delivery, driven by an obsessive commitment to security, scalability, and execution. We transform complex requirements into robust, market-ready systems.
Our capabilities span the full product lifecycle:
- Product Strategy and System Architecture: We help you define a technical roadmap, select the right tech stack, and architect a resilient system that’s built to grow with you.
- Secure Smart Contract Engineering: Our team develops and audits smart contracts using institutional-grade security practices, including comprehensive VAPT and integrated DevSecOps.
- Scalable Backend Infrastructure: We build the critical off-chain infrastructure that every decentralised application needs to perform reliably under real-world pressure.
We have deep, hands-on experience building platforms for decentralised trading, RWA tokenisation, and prediction markets—some of the fastest-growing sectors in Web3. The opportunity is massive. For example, India has been the world leader in crypto adoption for three straight years, with an estimated 119 million active users. What’s truly remarkable is that this growth is grassroots, with 75% of activity originating from non-metro cities. This opens up a huge, underserved market for new decentralised platforms. You can discover more insights about India’s crypto adoption here.
Whether you need a full delivery partner to build your vision from the ground up or a dedicated team to augment your existing roadmap, Blocsys brings the focused expertise required to execute effectively.
Ready to bring your Web3 vision to life? Connect with our experts today to discuss your project and learn how we can help you build, scale, and succeed.
Your Questions About Web3, Answered
As founders and developers start digging into Web3, a few common questions always come up. Let’s clear the air and tackle the big ones to give you a solid footing as you think about building in this space.
Is Web3 Just About Cryptocurrency and NFTs?
No. While cryptocurrencies and NFTs are prominent early applications, Web3 is the underlying technological foundation that makes them possible. The core innovation is the decentralized infrastructure—blockchains, smart contracts, and user-controlled wallets—that enables verifiable digital ownership. This architecture supports a wide range of solutions, including decentralized finance (DeFi), supply chain management, and community-governed organizations (DAOs).
How Is Web3 Different From the Metaverse?
Web3 is the technology layer, while the metaverse is a vision for an immersive, interconnected digital world. Web3 provides the fundamental building blocks—like provable ownership through NFTs and decentralized economic systems—that can power an open and user-owned metaverse. In short, Web3 is the “how” (the infrastructure), and the metaverse is the “what” (the experience).
What Are the Biggest Challenges to Web3 Adoption?
The primary obstacles to widespread Web3 adoption are user experience (UX), scalability, and regulatory uncertainty. Onboarding remains complex compared to Web2 applications, creating a barrier for mainstream users. While Layer-2 solutions are improving scalability, networks must still evolve to handle mass-market transaction volumes efficiently. Additionally, the evolving global regulatory landscape creates ambiguity for builders and investors.
Web3’s core challenges aren’t about what’s technologically possible—they’re engineering and adoption problems waiting to be solved. Cracking the code on UX and scalability is what will unlock its true mainstream potential.
How Do I Choose the Right Blockchain for My Project?
There’s no single “best” chain; the right choice is completely dependent on what you’re building. You’ll need to weigh the trade-offs between a few key factors:
- Security: How decentralised is the network? Is it proven and battle-tested against attacks?
- Scalability: Can it handle the transaction volume and speed your application will need?
- Ecosystem: Is there a healthy community of developers, tools, and users already there?
- Cost: How much will it cost your users to make transactions (i.e., gas fees)?
A platform like Ethereum gives you unmatched security and a massive ecosystem, but you’ll pay for it in speed and cost. On the other hand, chains like Solana or Polygon are often picked for projects that need higher throughput and lower fees.
Navigating these decisions is exactly where a specialised engineering firm like Blocsys Technologies comes in. We help organisations cut through the complexity to build and scale production-ready Web3 platforms. Whether you’re architecting a secure DeFi protocol, a system for real-world asset tokenisation, or a high-volume trading platform, our team has the end-to-end expertise to bring your vision to life.
Ready to build the future of decentralised infrastructure? Connect with our experts at Blocsys today for a strategic consultation.

1 Comment
Hi! I’ve been reading your web site for a long time now and finally got the courage to go ahead and
give you a shout out from Kingwood Tx! Just wanted
to mention keep up the good job!